The chemical compounds that are important for understanding most of the chemistry in this course are organic - that means that the compounds primarily contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (also sulfur and nitrogen). They can also be called hydrocarbons. The basic structures that we will be discussing in this course are called: 1) alkane (aka aliphatic), 2) branched alkane, 3) cycloalkane, 4) alkenes (double-bonds), 5) aromatic, 6) hydroaromatic, and 7) alcohols. First, I will show the atoms and how they are connected using the element abbreviation and lines as bonds, and then I will show abbreviated structural representations.
| Name | Atoms and Bonds | Stick Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Heptane (7 C atoms) |  | 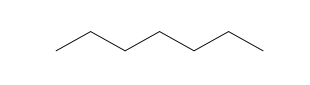 |
| Name | Atoms and Bonds | Stick Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Isobutane (4 C atoms) |  | 
|
| Isopentane (5 C atoms) |  |  |
| Name | Atoms and Bonds | Stick Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Cyclohexane (6 C atoms) |  |  |
| Name | Atoms and Bonds | Stick Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Pentene (5 C atoms) | 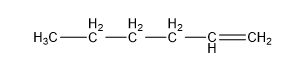 | 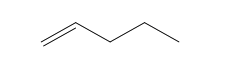 |
| Name | Atoms and Bonds | Stick Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Benzene (6 C atoms) | 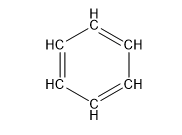 | 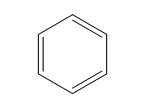 |
| Name | Atoms and Bonds | Stick Representation |
|---|---|---|
| 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene, aka tetralin (10 C atoms) | 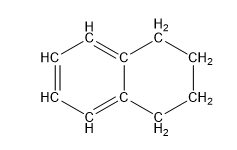 | 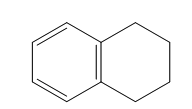 |
| Name | Atoms and Bonds | Stick Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Butanol (4 C atoms) |  |  |
| Ethanol (2 C atoms) |  |  |
The following table shows common hydrocarbons and their properties. It is important to know the properties of various hydrocarbons so that we can separate them and make chemical changes to them. This is a very brief overview - we will not yet be going into significant depth as to why the differences in chemicals affect the properties.
| Name | Number of C Atoms | Molecular Formula | bp (°C), 1 atm | mp (°C) | Density (g/mL) (@20°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methane | 1 | CH4 | -161.5 | -182 | -- |
| Ethane | 2 | C2H6 | -88.6 | -183 | -- |
| Propane | 3 | C3H8 | -42.1 | -188 | -- |
| Butane | 4 | C4H10 | -0.5 | -138 | -- |
| Pentane | 5 | C5H12 | 36.1 | -130 | 0.626 |
| Hexane | 6 | C6H14 | 68.7 | -95 | 0.659 |
| Heptane | 7 | C7H16 | 98.4 | -91 | 0.684 |
| Octane | 8 | C8H18 | 125.7 | -57 | 0.703 |
| Nonane | 9 | C9H20 | 150.8 | -54 | 0.718 |
| Decane | 10 | C10H22 | 174.1 | -30 | 0.730 |
| Tetradecane | 14 | C14H30 | 253.5 | 6 | 0.763 |
| Hexadecane | 16 | C16H34 | 287 | 18 | 0.770 |
| Heptadecane | 17 | C17H36 | 303 | 22 | 0.778 |
| Eicosane | 20 | C20H42 | 343 | 36.8 | 0.789 |
| Cyclohexane | 6 | C6H12 | 81 | 6.5 | 0.779 |
| Cyclopentane | 5 | C5H10 | 49 | -94 | 0.751 |
| Ethanol | 2 | C2H6O | 78 | -114 | 0.789 |
| Butanol | 4 | C4H10O | 118 | -90 | 0.810 |
| Pentene | 5 | C5H10 | 30 | -165 | 0.640 |
| Hexene | 6 | C6H12 | 63 | -140 | 0.673 |
| Benzene | 6 | C6H6 | 80.1 | 5.5 | 0.877 |
| Naphthalene | 10 | C10H8 | 218 | 80 | 1.140 |
| 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalene | 10 | C10H12 | 207 | -35.8 | 0.970 |